Modbus Addressing
Modbus Addressing
The address of any Tag that belongs to a Modbus data source should follow the following syntax format:
<Function Code>;<Index>
Following are different examples:
- Holding Registers (Words): Starts with 4
Examples:
4;1
4;120
- Bit Of Word:
Examples:
4;1.0
4;1.15
- Reading Floats (Double Words):
To read/write float variables (two words) or integers larger than (32,767), specify the address of the first word and choose the Data Type: Real
Example: 4;1 and Data Type Real means to read both the holding registers 1 and 2
- Reading Long Integers (Double Words):
To read/write long integers (32 bit), specify the address of the first word, choose the Data Type: Integer and enter 2 in word count.
Example: 4;9 and Data Type Integer (and word count = 2) means to read both the holding registers 9 and 10
- Coils: Start with 0
Examples:
0;1
0.324
Note: Coils are only supported in Modbus TCP client driver (Master) and not supported in Modbus Server.
- Input Registers: Starts with 3
Example: 3;1
- Input Floats: Starts with 3
Example: 3;1 and data type is Real
- Input Status: Starts with 1
Example: 1;1
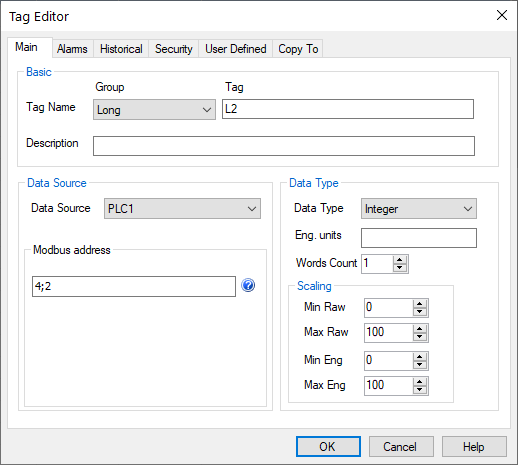
Example screen shots
1. One word at 400002
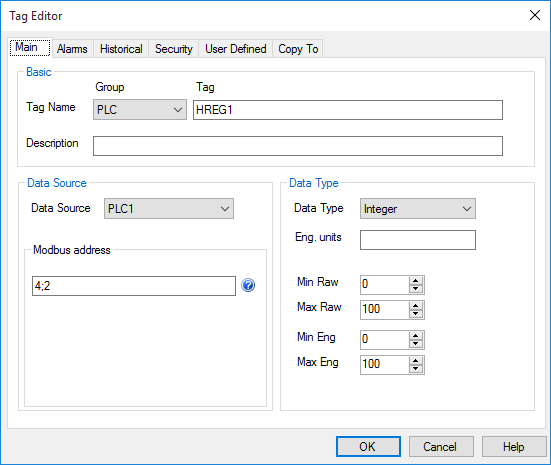
2. Double word at 400002
Example: 1;1This reads both word 400001 and 400002