Calculation Syntax
Calculation Tag Syntax (Also the same Syntax used in graphics animations).
The syntax of any Tag that belongs to a Calculation data source should follow the following syntax format:
- Getting Tag value:
- Example: LINE1.FT101 or Val(LINE1.FT101)
- Getting Tag status:
- Example: Status(LINE1.FT101)
- Getting a tag parameter: GetTagParam(TagName,TagParameter)
Examples:
- Get Tag's description: GetTagParam(LINE1.FT101,Description)
- Get Tag's data source name: GetTagParam(LINE1.FT101,DataSource)
- Get Tag's user defined 1 parameter: GetTagParam(LINE1.FT101,Description)
Note: The easiest way to know tag's parameters names is from the exported tag's sheet.
- Check if Tag status is Normal:
- Example: IsNormal(LINE1.FT101)
- Check if Tag status is High High:
- Example: IsHH(LINE1.FT101)
- Check if Tag status is High:
- Example: IsHi(LINE1.FT101)
- Check if Tag status is Low:
- Example: IsLo(LINE1.FT101)
- Check if Tag status is Low Low:
- Example: IsLL(LINE1.FT101)
- Check if Tag status is Initialized:
- Example: IsInitialized(LINE1.FT101)
- Check if Tag status is Unackknowleged:
- Example: IsUnAcked(LINE1.FT101)
- Getting Tag time stamp of last update:
- Example: TSTMAP(LINE1.FT101)
- Using a Tag value inside an expression: Use VAL(TagName) function.
Example: VAL(LINE1.FT101) > 2
- Dynamic parameters should be surrounded with curly parentheses.
Example: {TAG}
Example: VAL({TAG}) > 2
Example: VAL((GROUP}.TOTAL) > 2
- String comparison needs to be surrounded with single quotations.
Example: 'VAL(LINE1.STATUS)' = 'RUNNING'
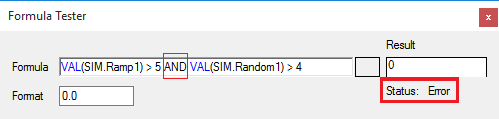
- 'and', 'or', and 'not': Logical operators used to evaluate conditions.
Note: These operators must be in lowercase.
Examples:
VAL(SIM.Ramp1) > 5 and VAL(SIM.Random1) > 4
VAL(SIM.Ramp1) > 5 or VAL(SIM.Random1) > 4
not (VAL(SIM.Ramp1))
VAL(SIM.Ramp1) > 5 and not (VAL(SIM.Random1) > 4)
- if statement
Syntax: if(condition, 'value is true', 'value is false')
Example: if(VAL(GROUP.TAG1) > 0, VAL(GROUP.TAG1), 0)
This result of this formula will equal to the value of "GROUP.TAG1" unless the value is below Zero. In this case, it'll equal Zero.
- 'Max' and 'Min': Returns the larger ('Max') or smaller ('Min') of two specified inputs.
Example: Max(VAL(SIM.Ramp1), VAL(SIM.Random1))
- 'Round': Rounds a value to the nearest integer or to the specified number of decimal places.
Example: Round(VAL(SIM.Ramp1), 2)
- 'Ceiling': Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to the specified input.
Example: Ceiling(VAL(SIM.Ramp1))
- 'Floor': Returns the largest integer less than or equal to the specified input.
Example: Floor(VAL(SIM.Ramp1))
- 'Abs': Returns the absolute value of a specified input.
Example: Abs(VAL(SIM.Ramp1))
- 'Sin', 'Cos', 'Tan', 'Asin', 'Acos', 'Atan': Returns the result of the specified trigonometric function applied to the input.
Example: Sin(VAL(SIM.Ramp1))
- 'Truncate': Removes the fractional part of a specified value, returning only the integer portion.
Example: Truncate(VAL(SIM.Ramp1))
- 'Sqrt': Returns the square root of a specified input.
Example: Sqrt(VAL(SIM.Ramp1))
- 'Pow': Raises a specified base to the power of a specified exponent.
Example: Pow(VAL(SIM.Ramp1), 2)
- Ln', 'Log', and 'Log10': Return the natural logarithm ('Ln'), logarithm with a specified base ('Log'), or base-10 logarithm ('Log10') of a specified input.
Example: Ln(VAL(SIM.Ramp1))
- 'Exp': Returns e (the base of natural logarithms) raised to the specified power.
Example: Exp(VAL(SIM.Ramp1))
- 'IEEERemainder': Returns the remainder resulting from the division of one specified number by another.
Example: IEEERemainder(VAL(SIM.Ramp1), 2)
- 'Sign': Returns a value indicating the sign of a number: -1 for negative, 0 for zero, and 1 for positive.
Example: Sign(VAL(SIM.Ramp1))
- Special keywords:
- $TIME: Gets the current time
- $DATE: Gets the current date
- $CURRENT_WIN: Gets the current opened graphical window's name
- $CURRENT_USER: Gets the current logged user's name
- $CURRENT_ACCESSLEVEL: Gets the current logged user's access level
- $SERVER_CONNECT_STATUS: Returns 1 if server is connected
- Special functions:
- IsServerConnected(): Returns 1 if server is connected
- GetConnectedServerIP(): Returns IP address of the connected server
- VAL_AND_UNIT(arg1, arg2, arg3)
arg1: Tag name
arg2: Number format (See examples below)
arg3: Unit (This can be any string).
Example: VAL_AND_UNIT(VAL(LINE1.FT101),'0.0','m3')
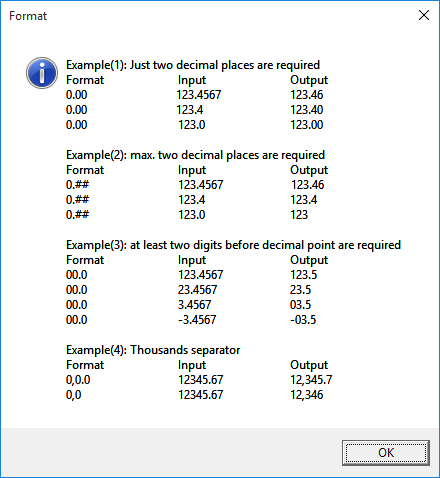
- Text formatting examples:
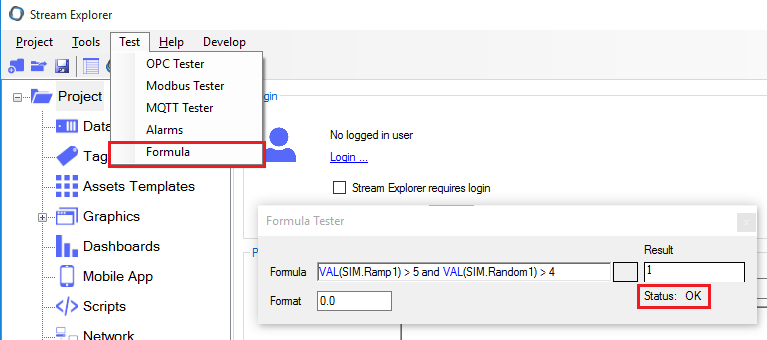
- You can use "Formula Tester" to test your formulas as below:
In the below example, the syntax is wrong (because 'and' is in capital letters):